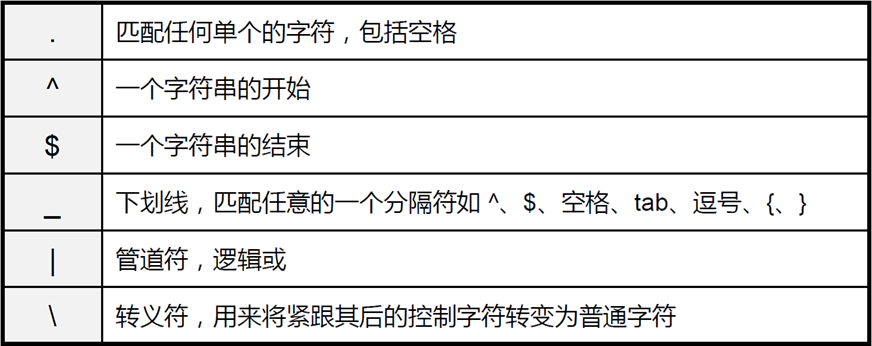
AS
- 属于同一个组织管理下的网络集合称为自制系统
- 一个自制系统往往具有相同的路由管理规范和策略
- AS通过不同的AS号进行区分,AS号范围原本范围是0-65535,后来进行扩展0-2^32^
- 中国电信163 AS号:4134
- 中国电信CN2 AS号:4809
- 中国网通AS 号:9929
IGP
- 内部网关协议
- 执行拓扑发现
- 当网络发生变化的时候,可以快速的更新路由
- 尽力完成快速收敛
- 网络发生变化,到全部设备的路由表都稳定的时间,称为收敛时间
- IGP协议的收敛速度是路由协议优化的一个衡量标准
- 需要周期性的更新来确保路由选择信息的精确性
- 受同一个管理机构的控制
- 采取了共同的路由选择策略
- 提供了优先的策略控制能力
- 控制路由的唯一手段就是度量值
EGP
- 外部网关协议
- 早期的时候有协议就叫EGP,后来被淘汰,被BGP替代
- 外部网关协议主要是为了在AS之间传递路由
- EGP的路由设备可能各自属于不同的自制系统
BGP
- Border Gateway Protocol 边界网关路由协议(距离矢量)
- 主要作用是在AS之间传递路由信息
- 目前BGP有4个版本:V1、V2、V4、V4+(即MBGP)
- 大量路由需要承载,IGP只能容纳千条,而BGP可以容纳上万
- 支撑MPLS/VPN的应用,传递客户VPN路由。
- 策略能力强,可以很好的实现路由决策与数据控制。
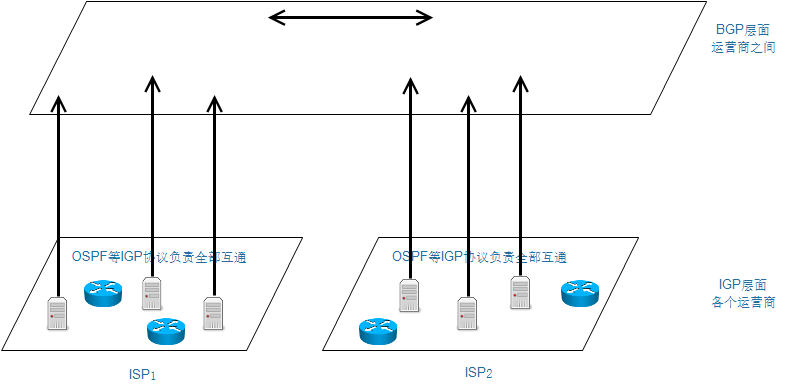
- 比如各个运营商将自己内部的服务地址通过BGP传递到全球,这样不同的运营商都可以访问。
- 一般来说各个AS不会将所有的地址都上报给BGP
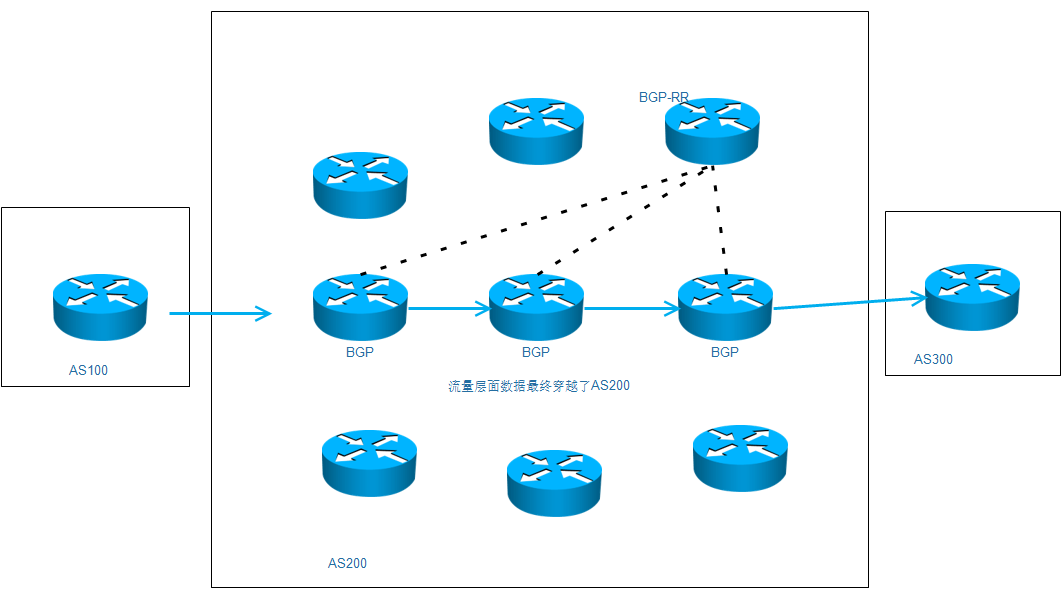
BGP机房
- 不是BGP机房的地址在不同地方访问可能会绕路,或者不通。
- BGP机房会通过BGP协议传递路由条目,让访问者的路由可以得到最佳的优化。
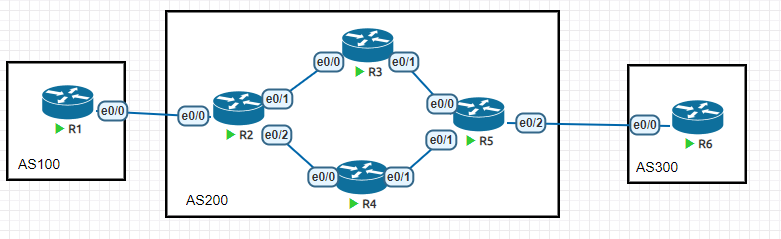
拓扑
IP地址配置
R1(config)#int lo0
R1(config-if)#ip add 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#int e0/0
R1(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no sh
==============================
R2(config)#int lo0
R2(config-if)#ip add 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#int e0/0
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#int e0/1
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
R2(config-if)#int e0/2
R2(config-if)#ip add 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no sh
==========================
R3(config)#int lo0
R3(config-if)#ip add 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#int e0/0
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
R3(config-if)#int e0/1
R3(config-if)#ip add 192.168.35.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no sh
==============================
R4(config)#int lo0
R4(config-if)#ip add 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#int e0/0
R4(config-if)#ip add 192.168.24.4 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no sh
R4(config-if)#int e0/1
R4(config-if)#ip add 192.168.45.4 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no sh
=============================
R5(config)#int lo0
R5(config-if)#ip add 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.0
R5(config-if)#int e0/0
R5(config-if)#ip add 192.168.35.5 255.255.255.0
R5(config-if)#no sh
R5(config-if)#int e0/1
R5(config-if)#ip add 192.168.45.5 255.255.255.0
R5(config-if)#no sh
R5(config-if)#int e0/2
R5(config-if)#ip add 192.168.56.5 255.255.255.0
R5(config-if)#no sh
===========================
R6(config)#int lo0
R6(config-if)#ip add 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.0
R6(config-if)#int e0/0
R6(config-if)#ip add 192.168.56.6 255.255.255.0
R6(config-if)#no shAS200中的IGP
这边要注意,在R2和R5的对其他AS的接口,不应启用路由协议,不然就会导致泄漏路由。
R2(config)#int range e0/1 -2 , lo0
R2(config-if-range)#ip ospf 1 area 0
===============================
R3(config-if)#int range e0/0 -1 , lo0
R3(config-if-range)#ip ospf 1 area 0
================================
R4(config-if)#int range e0/0 -1 , lo0
R4(config-if-range)#ip ospf 1 area 0
==================================
R5(config)#int range e0/0 -1 , lo0
R5(config-if-range)#ip ospf 1 area 0配置AS之间的BGP协议
首先建立R1和R2的BGP邻居
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.12.2 remote-as 200
# BGP无法自己发现邻居,因为BGP就不是拿来做拓扑发现作用的,是用来传递现有的路由
================================
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.12.1 remote 100查看邻居关系
R1#sh ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 1.1.1.1, local AS number 100
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
192.168.12.2 4 200 4 4 1 0 0 00:00:09 0
# 一定要确认Up/Down下面有时间,因为BGP summary中会显示所有被指定的邻居,即使从来没建立过
# 所以邻居条目即使有,后面写的never也是无效建立R5和R6的邻居
R5(config)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.56.6 remote 300
=======================
R6(config)#router bgp 300
R6(config-router)#neighbor 192.168.56.5 remote 300
# 这边如果AS号写错了,比如我写成了300
*Apr 5 02:32:30.617: %BGP-3-NOTIFICATION: sent to neighbor 192.168.56.5 passive 2/2 (peer in wrong AS) 2 bytes 00C8
# 如果出现了peer in wrong AS,就说明你配置错误的AS号查看邻居关系
R6#show ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 6.6.6.6, local AS number 300
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
192.168.56.5 4 200 5 5 1 0 0 00:01:28 0然而在AS之间建立连接,肯定是需要链路的冗余,所以直接指定对方的物理接口地址作为邻居也是不稳定的。
建议BGP所有的邻居关系都最好使用环回接口
AS之间不能启动IGP协议,但是可以配置静态路由,可以使用静态路由保障双方环回接口可达性。
R1(config)#ip route 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.12.2
=======================
R2(config)#ip route 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.12.1检查连通性
R1#ping 2.2.2.2 so 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 2.2.2.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 1.1.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms两边都设置邻居,并且设置更新源
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 remote 200
R1(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
=====================
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei 1.1.1.1 remote 100
R2(config-router)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0发现无法建立邻居
R1#sh ip bgp sum
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
2.2.2.2 4 200 0 0 1 0 0 never Idle我们尝试抓取EBGP邻居之间数据包
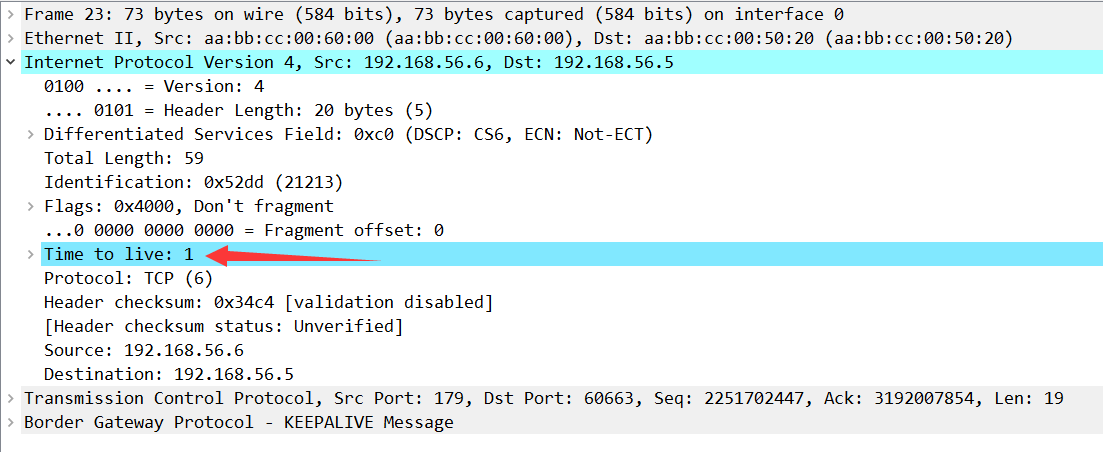
我们发现EBGP邻居默认发出的数据包TTL是1,也就是如果R1发送EBGP邻居消息给R2,根本无法被R2的lo0收到。
如果是EBGP邻居使用环回接口,或者跨网段建立邻居关系,需要设置EBGP多跳。
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop
=====================
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#neighbor 1.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop配置AS200内部的BGP协议
BGP使用端口号179/tcp来发送各种信息,消息基于4层传递,可以穿越广播域(之前的广播,组播都是不可以的),所以BGP可以跨设备建立邻居关系,在现实中也是这样,BGP设备在地理上可能处于不同的地方,但是可以互相建立邻居,最终组成覆盖全球大网。
R2和R5建立邻居就可以了,但是R5有两个接口都可以到达R2,那R2在指定邻居时候,选择R5的接口就比较重要。
由于物理接口的稳定性不如环回接口。所以我们一般使用环回接口作为BGP邻居地址。
比如R5的e0/0,e0/1任何一个接口失效了,R2依旧可以访问R5的环回接口。
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote 200
=======================
R5(config)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote 200等待一段时间之后,发现R2和R5无法建立邻居,通过debug bgp all,发现R5是通过192.168.45.5尝试与对方建立邻居的,但是R2只认5.5.5.5作为源地址。
*Apr 5 02:42:13.641: BGP: 2.2.2.2 open active, local address 192.168.45.5所以需要指定建立邻居的时候路由更新的源接口
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#neighbor 5.5.5.5 update-source lo0
===================
R5(config)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 up lo0检查邻居关系
R5#sh ip bgp summary
BGP router identifier 5.5.5.5, local AS number 200
BGP table version is 1, main routing table version 1
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
2.2.2.2 4 200 4 4 1 0 0 00:00:58 0
192.168.56.6 4 300 18 18 1 0 0 00:13:06 0BGP路由的传递
由于BGP并不是用来发现拓扑的,所以BGP在建立邻居的时候不会传递任何条目。
我们需要手动的将需要传递的路由加入BGP表,才可以被传递
我们将R1的lo0和R6的lo0作为通信的双方,将路由加入BGP表
R1(config)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
===============================================
R6(config)#router bgp 300
R6(config-router)#netw 6.6.6.0 mask 255.255.255.0在R2上检查路由
R2#show ip route bgp
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.0 [20/0] via 192.168.12.1, 00:01:18在R5上检查路由
R5#show ip route bgp
6.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 6.6.6.0 [20/0] via 192.168.56.6, 00:01:07发现R2和R5都各自学到了不同的路由,但是没有互相交换条目,检查R5的bgp表。
bgp表里面存放了BGP收到的所有条目,以及条目的属性,即使是无效的条目都会存在。
R5#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i 1.1.1.0/24 192.168.12.1 0 100 0 100 i
*> 6.6.6.0/24 192.168.56.6 0 0 300 iR5虽然收到了1.1.1.0/24条目,但是Next Hop无效。因为R5并不知道AS100中地址。
IGP是Router——Router的协议,所以在一个条目传递到下一台路由器的时候,下一跳会被改成之前路由器的地址。
BGP是AS——AS的协议,所以在一个条目传递到下一个AS的时候,下一跳会被改成之前AS的出去地址,BGP条目在AS内部传递的时候默认下一跳不变。
所以在AS边缘的路由器需要将条目的下一跳改为自己
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 next-hop-self
==================
R5(config)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 next-hop-self查看R5的BGP表,发现下一跳已经被改变
R5#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 100 i
*> 6.6.6.0/24 192.168.56.6 0 0 300 i查看R5的路由表
R5#sh ip route bgp
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.0 [200/0] via 2.2.2.2, 00:00:34
6.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 6.6.6.0 [20/0] via 192.168.56.6, 00:06:44查看R1和R6的路由表
R1#show ip route bgp
6.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 6.6.6.0 [20/0] via 192.168.12.2, 00:00:40
=========================
R6#sh ip route bgp
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.0 [20/0] via 192.168.56.5, 00:01:16尝试在R6上ping 1.1.1.1 source 6.6.6.6
结果并不通,逐条分析流量的源目的IP地址发现了原因。
当R1和R6互相通信的时候,R3和R4没有参与BGP,所以学不到BGP路由条目,当流量经过R3和R4的时候,就会被丢弃。
这个情况在BGP中很常见,我们称为路由黑洞,解决的方法有很多,看具体的情况。
BGP的邻居
R5#show ip bgp summary
Neighbor V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent TblVer InQ OutQ Up/Down State/PfxRcd
2.2.2.2 4 200 29 30 11 0 0 00:21:23 1
6.6.6.6 4 300 7 8 11 0 0 00:02:47 1- Neighbor
- 建立邻居的设备Router-ID
- V
- 版本,默认是v4
- AS
- 邻居所属的AS号
- MsgRcvd MsgSent
- 收到和发送的消息计数
- InQ OutQ
- 进站和出站队列,正常情况下是0
- 如果非0,表示网络发生拥塞
- Up/Down
- 邻居建立的时间
- 没有建立过的邻居会写never
State/PfxRcd
- 状态请参见下面的邻居状态表
- 前缀是表示从这个邻居学到的跳数数量
BGP显式的配置每个邻居,邻居之间建立TCP关系,默认每隔60S发送一次BGP/TCP存活消息,保持时间为180S
- BGP触发更新,增量更新
分类
- IBGP邻居关系
- 位于同一个自治系统的路由器之间的BGP邻接关系
- 建立IBGP邻接关系,满足的条件
- 自治系统号相同
- 定义邻居建立TCP会话
- IBGP邻居可达
- 这边测试可达性的时候,必须在ping后面加上source,因为BGP邻居看重源地址。
- EBGP邻居关系
- BGP位于不同自治系统的路由器之间的BGP邻接关系
- 建立EBGP邻接关系,必须满足三个条件
- EBGP之间自制系统号不同
- 定义邻居建立TCP会话
- neighbor中指定的IP地址要可达
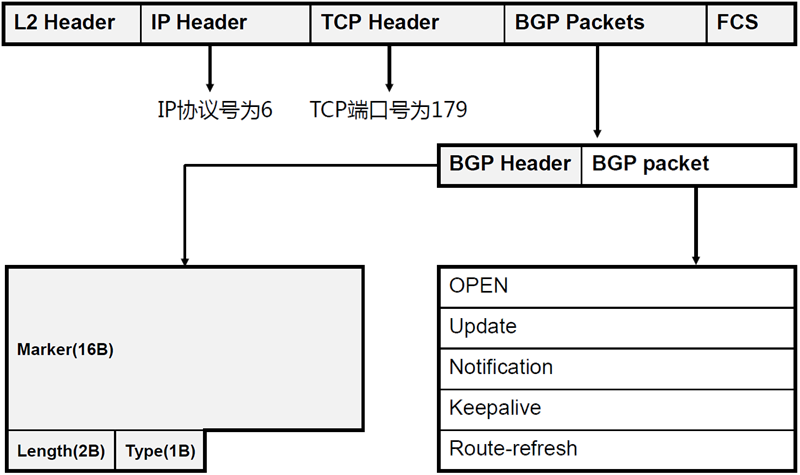
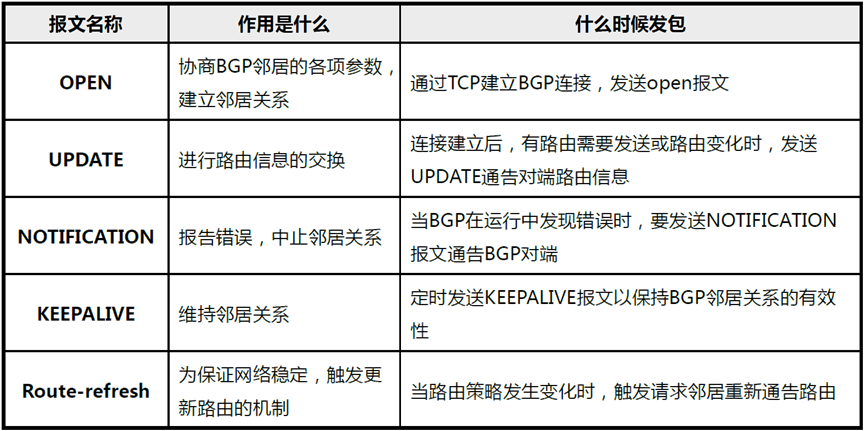
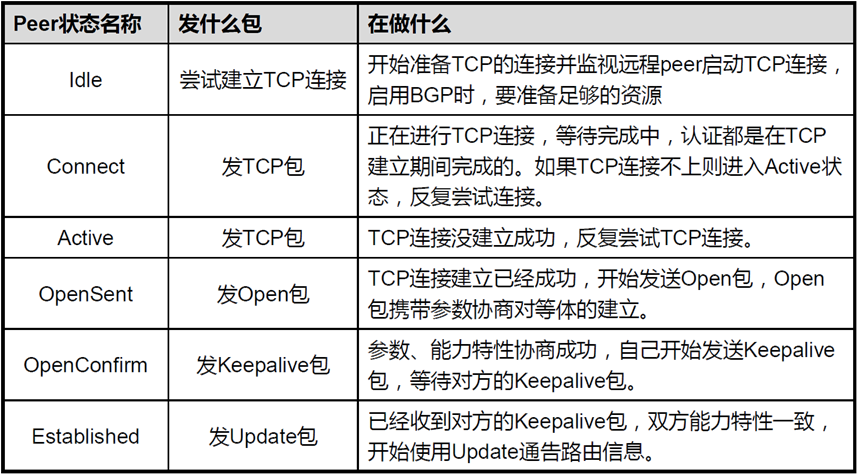
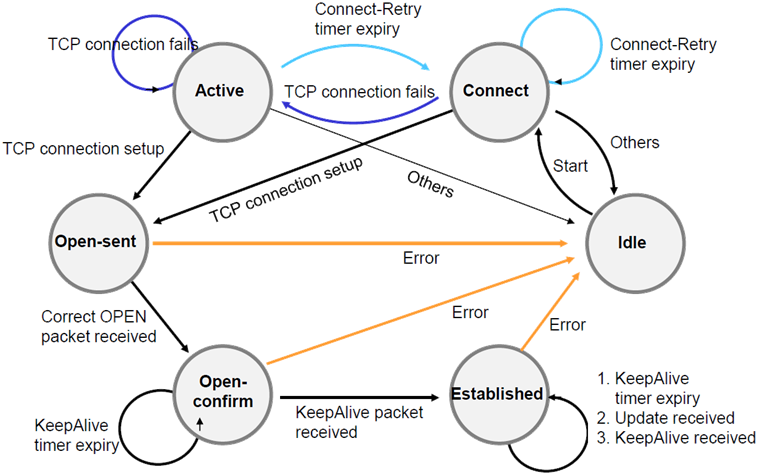
BGP消息类型
BGP同步
- BGP路由器不应使用通过IBGP获悉的路由或将其通告给外部邻居,除非该路由是本地的或通过IGP获悉的。
- 正常情况下,如果通过IGP学到了路由条目,就没必要用BGP了,所以BGP默认是关闭的,也不去打开
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#synchronizationBGP表
R5#show ip bgp
BGP table version is 11, local router ID is 5.5.5.5
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 100 i
*> 6.6.6.0/24 6.6.6.6 0 0 300 iBGP表中会保存着路由器通过BGP学习到所有路由条目和自己产生的BGP条目
- *
- 表示有效的
- >
- 最佳的,有了>才可以进入路由表
- i
- 表示是ibgp邻居发过来的
- Network
- 网段和前缀长度
- Next Hop
- 下一跳信息
- Metric
- 度量值
- 默认情况下本地产生的路由条目是0
- EBGP邻居传递过来的条目是空
- LocPrf
- 本地优先级
- 用于告知内部路由器如何优选离开本AS
- Weight
- 用于告诉自己如何选择最优路由
- 自己产生的条目权重为32768
- 学来的条目权重为0
- Path
- 里面记录了路由条目经历过的所有AS号
- 用来防止路由条目被自己重复学习了
- 最后的一个字母,表示了这条路由出身
- i
- 起源于IGP
- 是被管理员手动放进来的
- e
- 起源于egp协议(然而这个协议已经消失)
- ?
- 未知来源
- 比如重发布会丢失起源信息
- i
BGP维护
硬重置(很不推荐)
clear ip bgp *因为会删除所有BGP邻居,然后重新建立,由于BGP条目非常的多,这么做可能导致断网,或者导致邻居无法再次建立。
软重置(推荐)
R5#clear ip bgp * soft in/out软重置分为两种:
- in
- 发送route-refresh消息给邻居,然后邻居发送最新的路由条目,来刷新自己的路由表
- 这个过程中,在更新之前不会删除路由表条目
- out
- 发送route-refresh给邻居,告诉邻居我们要给你发送新的路由条目
- 邻居收到了之后可能会处理
BGP路由黑洞解决
路由黑洞在上面已经产生,解决方案多样
全互联
将R2-R3-R4-R5之间的直连线路都建立邻居关系
先删除R2-R5的邻居关系
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#no nei 5.5.5.5
=============
R5(config)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#no nei 2.2.2.2建立邻居关系
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei 3.3.3.3 remote 200
R2(config-router)#nei 3.3.3.3 up lo0
R2(config-router)#nei 3.3.3.3 next-hop-self
R2(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 remote 200
R2(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 up lo0
R2(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 next-hop-s
===================
R3(config)#router bgp 200
R3(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 remote 200
R3(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 up lo0
R3(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 remote 200
R3(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 up lo0
================
R4(config)#router bgp 200
R4(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 remote 200
R4(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 up lo0
R4(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 remote 200
R4(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 up lo0
===================
R5(config)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#nei ibgp peer-group
R5(config-router)#nei ibgp remote 200
R5(config-router)#nei ibgp next-hop-s
R5(config-router)#nei ibgp up lo0
R5(config-router)#nei 3.3.3.3 peer ibgp
R5(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 peer ibgp使用对等体组,将需要相同配置的邻居加入,可以简便配置。
下面我们检查R3和R4的路由表,发现可以学习到1.1.1.0/24和6.6.6.0/24
R3#sh ip route bgp
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.0 [200/0] via 2.2.2.2, 00:03:29
6.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 6.6.6.0 [200/0] via 5.5.5.5, 00:01:30
=============================
R4#sh ip route bgp
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.0 [200/0] via 2.2.2.2, 00:02:00
6.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 6.6.6.0 [200/0] via 5.5.5.5, 00:01:50下面检查R1—R6连通性
R1#ping 6.6.6.6 so 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 6.6.6.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 1.1.1.1
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)通过BGP表中的Path属性可以让路由条目在AS之间防环。但是在AS中,这个Path是不变的。所以BGP有ibgp水平分割的机制,来防止路由条目在AS内环路。
- 收到一个路由条目
- 如果是ebgp邻居给我的,那么将发送给所有的BGP邻居
- 如果是ibgp邻居给我的,那么将不会发送给任何一个ibgp邻居,只给ebgp邻居
可以在R2—-R5之间建立邻居关系,这样就可以学到路由条目了
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 remote 200
R2(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 up lo0
R2(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 next-hop-s
=====================
R5(config)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 peer ibgp检查连通性
R1#ping 6.6.6.6 so 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 6.6.6.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 1.1.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms但是全互联在实际应用中几乎无法实现,因为不是所有的设备都支持BGP的,即使支持BGP,性能也不够处理千万级别的条目。
而且全互联配置和维护极其麻烦,如果你有100台路由器,想全互联,那么需要建立9900个邻居关系,并且更新将会是一场网络风暴。
BGP路由重发布进IGP
删除AS200中的BGP
no router bgp 200然后R2和R5建立邻居关系
R2(config)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 remote 200
R2(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 up lo0
R2(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 next-hop-s
R2(config-router)#nei 1.1.1.1 remote 100
R2(config-router)#nei 1.1.1.1 up lo0
R2(config-router)#nei 1.1.1.1 eb
===================
R5(config)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 remote 200
R5(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 up lo0
R5(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 next-hop-s
R5(config-router)#nei 6.6.6.6 remote 300
R5(config-router)#nei 6.6.6.6 up lo0
R5(config-router)#nei 6.6.6.6 eb在R2和R5上重发布BGP条目到IGP中,让IGP学习到,来消除路由黑洞
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#redistribute bgp 200 subnets
============
R5(config)#router ospf 1
R5(config-router)#redistribute bgp 200 subnets检查R3R4的路由表
R3#sh ip route ospf
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 1.1.1.0 [110/1] via 192.168.23.2, 00:01:01, Ethernet0/0
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 2.2.2.2 [110/11] via 192.168.23.2, 00:05:10, Ethernet0/0
4.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 4.4.4.4 [110/21] via 192.168.35.5, 00:05:10, Ethernet0/1
[110/21] via 192.168.23.2, 00:05:10, Ethernet0/0
5.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 5.5.5.5 [110/11] via 192.168.35.5, 00:05:10, Ethernet0/1
6.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 6.6.6.0 [110/1] via 192.168.35.5, 00:00:40, Ethernet0/1
O 192.168.24.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.23.2, 00:05:10, Ethernet0/0
O 192.168.45.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.35.5, 00:05:10, Ethernet0/1
====================
R4#sh ip route ospf
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 1.1.1.0 [110/1] via 192.168.24.2, 00:01:18, Ethernet0/0
2.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 2.2.2.2 [110/11] via 192.168.24.2, 00:05:24, Ethernet0/0
3.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 3.3.3.3 [110/21] via 192.168.45.5, 00:05:24, Ethernet0/1
[110/21] via 192.168.24.2, 00:05:24, Ethernet0/0
5.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O 5.5.5.5 [110/11] via 192.168.45.5, 00:05:24, Ethernet0/1
6.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
O E2 6.6.6.0 [110/1] via 192.168.45.5, 00:00:57, Ethernet0/1
O 192.168.23.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.24.2, 00:05:24, Ethernet0/0
O 192.168.35.0/24 [110/20] via 192.168.45.5, 00:05:24, Ethernet0/1检查连通性
R1#ping 6.6.6.6 so 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 6.6.6.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 1.1.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms但是IGP在真实场景中,可能处理不了BGP庞大的路由条目,导致本职工作受到影响。
这样做了之后,也将外部的条目引入了内部路由协议,可能导致一系列问题。
路由反射器
删除R2R5的BGP邻居,并且删除重发布操作
R2(config)#router ospf 1
R2(config-router)#no redistribute bgp 200 subnets
R2(config-router)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#no nei 5.5.5.5
============
R5(config)#router ospf 1
R5(config-router)#no redistribute bgp 200 subnets
R5(config-router)#router bgp 200
R5(config-router)#no nei 2.2.2.2在发生ibgp水平分割无法将条目再次发送给ibgp邻居的时候,可以将对方设置为路由反射器客户端,这样就可以打破一次水平分割机制。
在实际应用中,我们在一个AS中,选择一个路由器作为反射器,然后其他的BGP路由全部都和这个反射器做邻居,有任何路由更新,都只发给反射器,再由反射器发送给所有的ibgp邻居。
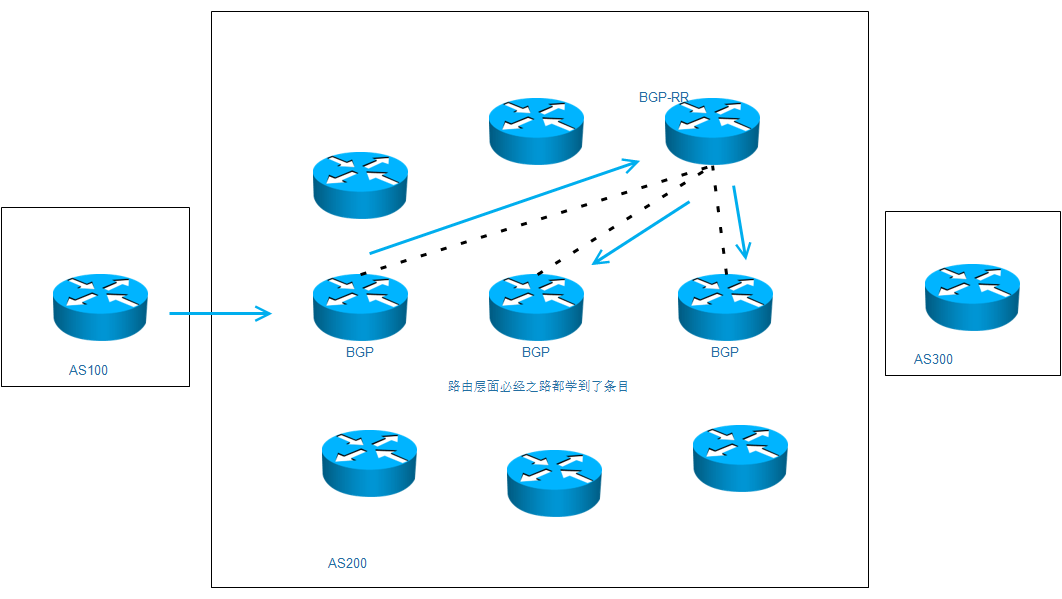
如果再由100台路由器,那么只需要挑选节点,和路由反射器建立邻居即可,即使都需要加入BGP,那也不过99个邻居关系。
下图是规则的补充
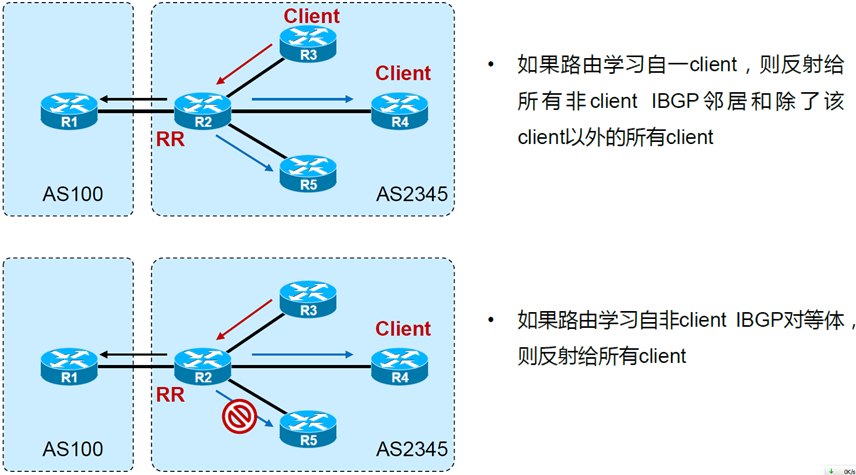
之前的路由黑洞实验,我们选择R3作为路由反射器,其他路由器都和R3建立邻居。
R2&R4&R5
router bgp 200
nei 3.3.3.3 remote 200
nei 3.3.3.3 up lo0
nei 3.3.3.3 next-hop-s # R4不需要这条
===============
R3
R3(config)#router bgp 200
R3(config-router)#nei as200 peer
R3(config-router)#nei as200 remote 200
R3(config-router)#nei as200 up lo0
R3(config-router)#nei as200 route-reflector-client
R3(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 peer as200
R3(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 peer as200
R3(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 peer as200检查连通性
R1#ping 6.6.6.6 so 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 6.6.6.6, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 1.1.1.1
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 msBGP联邦
本文后续介绍
BGP常见属性
BGP属性分类
- 公认属性 Well-Known(所有路由器都必须认识)
- 公认强制属性Well-known mandatory(所有路由在更新的时候,都必须携带,如果不携带,直接报错)
- 公认自由决定属性Well-known discretionary(可以更新的时候不携带)
- 可选属性 Optional(路由器可以不识别)
- 可选传递的Optional transitive(建议将这个属性传递下去)
- 可选非传递的Optional non-transitive(建议这个属性不传递)
拓扑
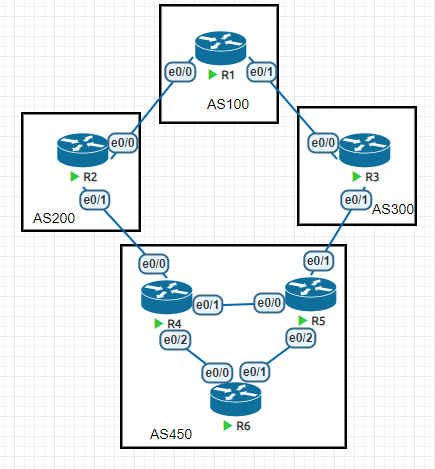
初始配置
===============R1===============
interface Loopback0
no shutdown
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 300
neighbor 3.3.3.3 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
ip route 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.12.2
ip route 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 192.168.13.3
===============R2===============
interface Loopback0
no shutdown
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
router bgp 200
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 2.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 450
neighbor 4.4.4.4 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
ip route 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.12.1
ip route 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 192.168.24.4
===============R3===============
interface Loopback0
no shutdown
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.13.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.35.3 255.255.255.0
router bgp 300
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 3.3.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote-as 450
neighbor 5.5.5.5 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 5.5.5.5 update-source Loopback0
ip route 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 192.168.13.1
ip route 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.255 192.168.35.5
===============R4===============
interface Loopback0
no shutdown
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.24.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.45.4 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.46.4 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
router bgp 450
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 4.4.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 6.6.6.6 remote-as 450
neighbor 6.6.6.6 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 6.6.6.6 next-hop-self
ip route 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 192.168.24.2
===============R5===============
interface Loopback0
no shutdown
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.45.5 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.35.5 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.56.5 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
router bgp 450
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 5.5.5.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 300
neighbor 3.3.3.3 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 6.6.6.6 remote-as 450
neighbor 6.6.6.6 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 6.6.6.6 next-hop-self
ip route 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 192.168.35.3
===============R6===============
interface Loopback0
no shutdown
ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.46.6 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
no shutdown
ip address 192.168.56.6 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
router bgp 450
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 6.6.6.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 450
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 route-reflector-client
neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote-as 450
neighbor 5.5.5.5 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 5.5.5.5 route-reflector-client权重(weight)
- 思科私有的,不过其他厂商也有,只是名字不一样
- 在路由器本地配置,只提供本地路由策略,不会传播给任何BGP邻居
- 范围:0~65535;越大越优先
- 路由器本地始发的路径默认权重为32768,从其他BGP邻居学习到的为0
查看R4关于1.1.1.1的bgp表,发现其实可以有两条路线去往,R4优选从2.2.2.2走。
R4#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i 1.1.1.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 100 i
*> 2.2.2.2 0 200 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i 5.5.5.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 i我们修改5.5.5.5这条路线的权重,可以影响R4的选路
R4(config)#router bgp 450
R4(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 weight 10
R4#clear ip bgp * so in
R4#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 10 300 100 i
* 2.2.2.2 0 200 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 10 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i 5.5.5.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 10 i可以看到凡是5.5.5.5学习的条目权重都被修改了,影响整个邻居,正常情况下不推荐使用。
R4(config)#router bgp 450
R4(config-router)#no nei 5.5.5.5 weight 10可以使用route-map对特定路由的权重进行修改
R4(config)#access-list 1 permit 1.1.1.0
R4(config)#route-map R5 per
R4(config-route-map)#mat ip ad 1
R4(config-route-map)#set weight 10
R4(config)#route-map R5 per 20
R4(config)#router bgp 450
R4(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 route-map R5 in
R4(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so in
R4(config-router)#do sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 10 300 100 i
* 2.2.2.2 0 200 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i 5.5.5.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 i本地优先级(local preference)
- 公认自由决定属性
- 告诉AS中的路由器,哪条路径是离开AS的首选路径
- LP越高路径越优
- 只发送给IBGP邻居,而不能传递给EBGP邻居
- 默认本地优先级为100
将上面的实验环境还原
R6#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i 1.1.1.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 100 i
*>i 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 200 100 i
*>i 2.2.2.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 i
*>i 4.4.4.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 i
*>i 5.5.5.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 i
*> 6.6.6.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i可以看到R6去往1.1.1.0/24可以有两个路线,现在选择的是4.4.4.4。我们可以在R5上略施手段让R6选择从R5走,在R5上修改更新给R6路由的本地优先级。
R5(config)#router bgp 450
R5(config-router)#bgp default local-preference 500
R5(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so out查看R6的BGP表
R6#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 500 0 300 100 i
*>i 2.2.2.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 500 0 300 i
*>i 4.4.4.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 i
*>i 5.5.5.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 500 0 i
*> 6.6.6.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i如果想设置某台路由器作为整个AS的优选出口,可以修改默认的本地优先级
如果只是想改某一条路由的路径,建议用route-map
R5(config)#access-list 1 permit 1.1.1.0
R5(config)#route-map R6 per
R5(config-route-map)#mat ip add 1
R5(config-route-map)#set local-preference 110
R5(config-route-map)#exit
R5(config)#route-map R6 per 20
R5(config-route-map)#router bgp 450
R5(config-router)#nei 6.6.6.6 route-map R6 out
R5(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so out查看R6的BGP表
R6#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 110 0 300 100 i
*>i 2.2.2.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 i
*>i 4.4.4.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 i
*>i 5.5.5.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 i
*> 6.6.6.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 iAS_PATH
- 公认强制属性
- 是前往目标网络的路由经过的自制系统号列表,通告该路由的自治系统号位于列表末尾
- 作用:确保无环,通告给EBGP时会加上自己的AS号;通告给IBGP时不修改AS-path
- 只有在AS之间传递的时候才会发生变化,如果AS_PATH中有自己的AS号,那么就不学习不传递
如果R1不想让AS450学习到1.1.1.0这个条目,我们可以在AS_PATH中手动加上AS450
首先在R2上查看一下1.1.1.0的AS_PATH,只有AS100
R2#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.1 0 0 100 i在R1上配置1.1.1.0离开AS100的route-map追加AS450
R1(config)#access-list 1 permit 1.1.1.0
R1(config)#route-map AS100out per
R1(config-route-map)#ma ip add 1
R1(config-route-map)#set as-path prepend 450
R1(config-route-map)#exit
R1(config)#route-map AS100out per 20
R1(config-route-map)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 route-map AS100out out
R1(config-router)#nei 3.3.3.3 route-map AS100out out
R1(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so out在R2上再次查看1.1.1.0的AS_PATH
R2#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.1 0 0 100 450 i我们发现AS450中就学习不到这个条目了
R6#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 2.2.2.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 200 i
*>i 3.3.3.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 i
*>i 4.4.4.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 i
*>i 5.5.5.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 i
*> 6.6.6.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 iAS_PATH也可以用于路径好坏的判断,如果去往同一个目的地,权重和本地优先级都一样,那么可能会根据AS_PATH长度来判断哪条路径最佳。AS_PATH越短表示离目的地越近,路线越优。
还原实验环境,查看R6的bgp表,我们通过修改AS_PATH长度来影响路线选择
R6#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 100 0 200 100 i
* i 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 100 i在R2上修改交给R4的1.1.1.0路由,增加AS_PATH长度,为了防止对其他的AS造成影响,所以推荐追加的AS号为自己的AS号,比如R2就追加200
R2(config)#access-list 1 permit 1.1.1.0
R2(config)#route-map R4out per
R2(config-route-map)#ma ip add 1
R2(config-route-map)#set as pre 200 200 200
R2(config-route-map)#route-map R4out per 20
R2(config-route-map)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 route-map R4out out
R2(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so out查看R4的BGP表
R4#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 100 i
* 2.2.2.2 0 200 200 200 200 100 iAS_PATH有4种
- 有序AS_PATH
- 正常的AS_PATH都是会按照顺序进行排列,称为有序
- 450 300 100 i
- 无序AS_PATH
- 如果将多个AS的多条路由条目进行汇总,这个汇总的路由携带的AS_PATH就可能是无序的
- 汇总路由的明细来自于AS300和AS100,不分先后,所以无序
- 450 {300 100} i
- 联邦内有序AS_PATH
- 联邦内无序AS_PATH
ORIGIN
- 公认强制属性
标识路由的起源,有下列3种可能:
- i 通过BGP network,也就是起源于IGP,因为BGP network必须保证该网络在路由表中
- e 是由 EGP 这种早期的协议重发布而来
- ? Incomplete,从其他渠道学习到的,路由来源不完全(确认该路由来源的信息不完全)。 (重发布的路由)
- 路由优选顺序: lowest origin code (IGP > EGP > Incomplete)
还原实验环境
R2(config)#access-list 1 per 1.1.1.0
R2(config)#route-map R4out per
R2(config-route-map)#mat ip ad 1
R2(config-route-map)#set origin incomplete
R2(config-route-map)#route-map R4out per 20
R2(config-route-map)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 route-map R4out out
R2(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so out查看R4上路径的选择
R4#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i 1.1.1.0/24 5.5.5.5 0 100 0 300 100 i
* 2.2.2.2 0 200 100 ?MED
- 可选非传递属性
- 是一种度量值,用于向外部邻居指出进入AS的首选路径,即当入口有多个时,自治系统可以使用MED动态的影响其他AS如何选择进入路径
- 度量值越小路径越优
- MED是在AS之间交换,MED发送给EBGP对等体,这些路由器在AS内传播MED,不传递给下一个AS
R1(config)#access-list 1 permit 1.1.1.0
R1(config)#route-map R2out per
R1(config-route-map)#ma ip add 1
R1(config-route-map)#set met
R1(config-route-map)#set metric 100
R1(config-route-map)#route-map R2oute per 20
R1(config-route-map)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 route-map R2out out
R1(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so查看修改的效果
R2#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.1 100 0 100 iBGP在重发布IGP条目的时候,会将IGP条目的度量值用作MED
R4(config)#access-list 1 permit 192.168.56.0
R4(config)#route-map o-b per
R4(config-route-map)#ma ip ad 1
R4(config-route-map)#router bgp 450
R4(config-router)#redistribute ospf 1 route-map o-b在R2上查看度量值,发现将OSPF的开销作为MED属性
R2#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 192.168.56.0 4.4.4.4 20 0 450 ?Next-Hop
- 公认必遵属性
- EBGP邻居之间传递的时候默认会修改下一跳为通告方
- IBGP邻居之间传递的时候,默认下一跳属性不会发生变化
- 建议在收到EBGP邻居更新条目转发给IBGP邻居的时候,加上Next-hop-self
- 不同的AS之间是用多路访问网络(MA)相连情况下,可以使用next-hop-unchange做到类似重定向的功能
Community(团体属性/社团属性)
- 可选传递属性
- 一种标记,用于简化路由策略的执行
- 可以将某些路由分配一个特定的COMMUNITY属性,之后就可以基于COMMUNITY值而不是每条路由进行BGP属性的设置了
还原实验环境
假设1.1.1.0/24、10.10.10.0/24是属于某公司的AB两个个部门。AS300需要对B部门的条目修改,不让AS450收到。做到让AS450优选从AS200去往这个部门。
A:标签100:1
B:标签100:2
一个条目可以携带多个标签,来标识不同的团体,可以是下面这样包含关系标签,可以指定不同的范围
银河系——太阳系——地球——亚洲——中国——江苏——镇江——京口区——学府路——江苏大学——物联网专业——18届
R1(config)#access-list 1 per 1.1.1.0
R1(config)#access-list 2 per 10.10.10.0
R1(config)#route-map R2R3out per
R1(config-route-map)#ma ip ad 1
R1(config-route-map)#set community 100:1
R1(config-route-map)#route-map R2R3out per 20
R1(config-route-map)#ma ip ad 2
R1(config-route-map)#set community 100:2
R1(config-route-map)#route-map R2R3oute per 30
R1(config-route-map)#router bgp 100
R1(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 route-map R2R3out out
R1(config-router)#nei 3.3.3.3 route-map R2R3out out
R1(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 send-community
R1(config-router)#nei 3.3.3.3 send-community
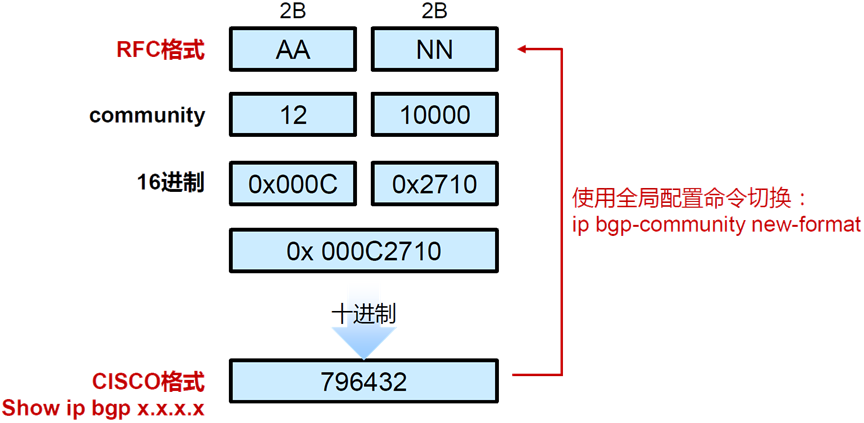
# 别忘了开启团体属性的发送查看团体属性
R3(config)#ip bgp-community new-format
R3(config)#do sh ip bgp 10.10.10.0
BGP routing table entry for 10.10.10.0/24, version 11
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table default)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 1
100
1.1.1.1 from 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, best
Community: 100:2
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0后面可以根据不同的community属性加上策略
R3(config)#ip community-list 1 permit 100:1
R3(config)#route-map R5out deny
R3(config-route-map)#match community 1
R3(config-route-map)#route-map R5out per 20
R3(config-route-map)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 route-map R5out out
R3(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so查看R5的bgp表,发现现在已经无法从R3学习到有100:1标签的路由了
R5#sh ip bgp 1.1.1.0
BGP routing table entry for 1.1.1.0/24, version 14
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table default)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 1
200 100
4.4.4.4 (metric 11) from 6.6.6.6 (6.6.6.6)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
Originator: 4.4.4.4, Cluster list: 6.6.6.6
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0有默认操作的团体属性
以下的属性是有默认功能的,不需要手动加上策略,携带了这个团体属性的条目默认就回执行对应的动作
<1-4294967295> community number
# 正常的团体属性
aa:nn community number in aa:nn format
# 正常的团体属性
internet Internet (well-known community)
# 表示所有的条目,如果想匹配any,可以用这个
local-AS Do not send outside local AS (well-known community)
# 不要让这个条目离开自己这个AS,也就是不会对EBGP邻居更新这个条目
no-advertise Do not advertise to any peer (well-known community)
# 告知下一个AS,不要让这个条目给第三个路由器知道
no-export Do not export to next AS (well-known community)
# 告知下一个AS,不要让这个条目给第三个AS知道
none No community attribute
# 去除所有community标签还原实验环境
让R6的6.6.6.0带上local-AS属性
R6(config)#access-list 1 permit 6.6.6.0
R6(config)#route-map R4R5out per
R6(config-route-map)#ma ip ad 1
R6(config-route-map)#set commu local-AS
R6(config-route-map)#route-map R4R5out per 20
R6(config-route-map)#router bgp 450
R6(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 route-map R4R5out out
R6(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 route-map R4R5out out
R6(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 send-comm
R6(config-router)#nei 5.5.5.5 send-comm
R6(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so查看R4上的条目是否有这个属性
R4#sh ip bgp 6.6.6.0
BGP routing table entry for 6.6.6.0/24, version 12
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table default, not advertised outside local AS)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 2
Local
6.6.6.6 (metric 11) from 6.6.6.6 (6.6.6.6)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
Community: local-AS
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0查看其他AS是否能学习到6.6.6.0
R2#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.1 0 0 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 3.3.3.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 450 300 i
*> 1.1.1.1 0 100 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 0 450 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 450 i
* 1.1.1.1 0 100 300 450 i让6.6.6.0携带上no-advertise
R6(config)#route-map R4R5out per 10
R6(config-route-map)#no set commu local-AS
R6(config-route-map)#set commu no-adv查看R4是否有这个属性
R4#sh ip bgp 6.6.6.0
BGP routing table entry for 6.6.6.0/24, version 13
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table default, not advertised to any peer)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 4
Local
6.6.6.6 (metric 11) from 6.6.6.6 (6.6.6.6)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
Community: no-advertise
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0然后查看R2是否学习到
R2#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 1.1.1.1 0 0 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* 3.3.3.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 450 300 i
*> 1.1.1.1 0 100 300 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 0 450 i
*> 5.5.5.0/24 4.4.4.4 0 450 i
* 1.1.1.1 0 100 300 450 i还原实验环境,在R4通告R2的时候让6.6.6.0携带上no-advertise
R4(config)#access-list 1 per 6.6.6.0
R4(config)#route-map R2 per
R4(config-route-map)#ma ip ad 1
R4(config-route-map)#set commu no-ex
R4(config-route-map)#route-map R2 per 20
R4(config-route-map)#router bgp 450
R4(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 route-map R2 out
R4(config-router)#nei 2.2.2.2 send-comm
R4(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so查看R2是否有这个属性
R2#sh ip bgp 6.6.6.0
BGP routing table entry for 6.6.6.0/24, version 8
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table default, not advertised to EBGP peer)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 1
100 300 450
1.1.1.1 from 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0
Refresh Epoch 1
450
4.4.4.4 from 4.4.4.4 (4.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external, best
Community: no-export
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0到R1上查看路由条目,发现已经不能从R2学到这个条目了
R1#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 0 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 0 300 i
* 4.4.4.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 300 450 i
*> 2.2.2.2 0 200 450 i
* 5.5.5.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 200 450 i
*> 3.3.3.3 0 300 450 i
*> 6.6.6.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 300 450 i如果AS200想让AS100继续可以学习到这个条目,也就是让no-export属性失效,可以进行如下操作
R2(config)#ip community-list 1 per no-export
R2(config)#access-list 1 per 6.6.6.0
R2(config)#route-map R4 per
R2(config-route-map)#ma ip add 1
R2(config-route-map)#set comm-list 1 delete
R2(config-route-map)#route-map R4 per 20
R2(config-route-map)#router bgp 200
R2(config-router)#nei 4.4.4.4 route-map R4 in
R2(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so in查看R2上6.6.6.0的属性
R2#sh ip bgp 6.6.6.0
BGP routing table entry for 6.6.6.0/24, version 9
Paths: (2 available, best #2, table default)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 3
100 300 450
1.1.1.1 from 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0
Refresh Epoch 3
450
4.4.4.4 from 4.4.4.4 (4.4.4.4)
Origin IGP, localpref 100, valid, external, best
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0查看R1是否可以学习到这个条目
R1#sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 8, local router ID is 1.1.1.1
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 0 200 i
*> 3.3.3.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 0 300 i
* 4.4.4.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 300 450 i
*> 2.2.2.2 0 200 450 i
* 5.5.5.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 200 450 i
*> 3.3.3.3 0 300 450 i
* 6.6.6.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 200 450 i
*> 3.3.3.3 0 300 450 iBGP路由汇总
在R1上配置172.16.10.1/24、172.16.11.1/24两个环回接口
在R2上配置172.16.20.1/24、172.16.21.1/24两个环回接口
下面是初始的配置
===============R1=============
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback10
ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback11
ip address 172.16.11.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 172.16.10.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.11.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 192.168.13.3 remote-as 300
===============R2=============
interface Loopback10
ip address 172.16.20.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Loopback11
ip address 172.16.21.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 200
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 172.16.20.0 mask 255.255.255.0
network 172.16.21.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 192.168.23.3 remote-as 300
===============R3=============
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.13.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
ip address 192.168.34.3 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 300
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 192.168.13.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 192.168.23.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 192.168.34.4 remote-as 400
===============R4=============
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.34.4 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 192.168.34.3 remote-as 300检查,在R4上可以看到4条明细的BGP路由条目
R4#sh ip route bgp
172.16.0.0/24 is subnetted, 4 subnets
B 172.16.10.0 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:02:35
B 172.16.11.0 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:02:35
B 172.16.20.0 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:02:35
B 172.16.21.0 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:02:35在R3上对172开头的4个条目进行汇总
R3(config)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0查看R4的BGP路由表,发现明细和汇总都能学到,因为BGP的汇总命令只是产生汇总路由,而不抑制明细路由更新
R4#sh ip route bgp
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 2 masks
B 172.16.0.0/16 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:00:22
B 172.16.10.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:03:38
B 172.16.11.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:03:38
B 172.16.20.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:03:38
B 172.16.21.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:03:38在R3上配置抑制明细路由
R3(config)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only 查看R3的BGP表,前面有s标记的条目就是被抑制了
R3(config-router)#do sh ip bgp
BGP table version is 10, local router ID is 3.3.3.3
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale, m multipath, b backup-path, f RT-Filter,
x best-external, a additional-path, c RIB-compressed,
t secondary path,
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
RPKI validation codes: V valid, I invalid, N Not found
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.0 32768 i
s> 172.16.10.0/24 192.168.13.1 0 0 100 i
s> 172.16.11.0/24 192.168.13.1 0 0 100 i
s> 172.16.20.0/24 192.168.23.2 0 0 200 i
s> 172.16.21.0/24 192.168.23.2 0 0 200 i查看R4的路由表和BGP表
R4#sh ip route bgp
B 172.16.0.0/16 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:03:06
R4#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.0.0 192.168.34.3 0 0 300 iR4学到的这条汇总路由AS_PATH被篡改,这样很可能让这条汇总路由,被明细所在的AS学习到,导致潜在的环路风险。
R2#sh ip route bgp
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 5 subnets, 3 masks
B 172.16.0.0/16 [20/0] via 192.168.23.3, 00:04:47在R3上面汇总的时候,带上AS_PATH信息
R3(config)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 summary-only as-set查看R4的BGP表,发现了无序的AS_PATH属性
R4#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.0.0 192.168.34.3 0 0 300 {100,200} i检查AS100或者AS200,发现不会将汇总路由重新学习回去了
R2#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.20.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 172.16.21.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i由于AS300会抑制172.16开头的明细条目,所以AS100和AS200互相学习不到明细
如果我们想让AS100和AS200能够互相学习明细路由
在R3上针对不同的邻居,可以取消某些条目的抑制
R3(config)#access-list 1 permit 172.16.20.0
R3(config)#access-list 1 permit 172.16.21.0
R3(config)#access-list 2 permit 172.16.10.0
R3(config)#access-list 2 permit 172.16.11.0
R3(config)#route-map unsupp per
R3(config-route-map)#ma ip add 1
R3(config-route-map)#route-map unsup
R3(config-route-map)#route-map unsupp per 20
R3(config-route-map)#ma ip add 2
R3(config-route-map)#exit
R3(config)#route-map unsupp per 30
R3(config-route-map)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.1 unsuppress-map unsupp
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.2 unsuppress-map unsupp检查R1和R2的路由表
R1#sh ip route bgp
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks
B 172.16.20.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:25
B 172.16.21.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.13.3, 00:00:25R2#sh ip route bgp
172.16.0.0/16 is variably subnetted, 6 subnets, 2 masks
B 172.16.10.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.23.3, 00:00:58
B 172.16.11.0/24 [20/0] via 192.168.23.3, 00:00:58上面的需求是取消某些条目的抑制,如果我们只是想抑制部分,可以这样做
还原实验环境
R3(config)#access-list 1 per 172.16.11.0
R3(config)#access-list 1 per 172.16.21.0
R3(config)#route-map supp per
R3(config-route-map)#ma ip ad 1
R3(config-route-map)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#ag
R3(config-router)#aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 as-set suppress-map supp查看R3的bgp表,确认部分被抑制
R3#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.0.0 0.0.0.0 100 32768 {100,200} i
*> 172.16.10.0/24 192.168.13.1 0 0 100 i
s> 172.16.11.0/24 192.168.13.1 0 0 100 i
*> 172.16.20.0/24 192.168.23.2 0 0 200 i
s> 172.16.21.0/24 192.168.23.2 0 0 200 i如果明细消失了,那么汇总也要跟着消失,在R3上模拟R1和R2邻居断开,导致明细丢失
R3(config)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.13.1 shutdown
R3(config-router)#nei 192.168.23.2 shutdown查看R4的BGP表,在BGP中,默认明细丢失了,也不影响汇总条目的通告,这个是有问题
R4#sh bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 172.16.0.0 192.168.34.3 0 0 300 200 i可以配置advertise-map让BGP做到明细丢失了,就把汇总也删除。
R3(config)#access-list 1 per 172.16.11.0
R3(config)#access-list 1 per 172.16.21.0
R3(config)#route-map adv per
R3(config-route-map)#ma ip ad 1
R3(config-route-map)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#ag
R3(config-router)#aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 as-set advertise-map adv检查R4的BGP表
R4#sh bgp另外在汇总路由条目的属性中会携带汇总的属性(atomic-aggregate属性),里面会标识汇总节点的BGP Router-ID
R3(config-route-map)#router bgp 300
R3(config-router)#no nei 192.168.23.1 shu
R3(config-router)#no nei 192.168.23.2 shu查看R4的BGP表中明细条目的属性
R4#show bgp 172.16.0.0
BGP routing table entry for 172.16.0.0/16, version 24
Paths: (1 available, best #1, table default)
Not advertised to any peer
Refresh Epoch 1
300 100, (aggregated by 300 3.3.3.3)
192.168.34.3 from 192.168.34.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, external, atomic-aggregate, best
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0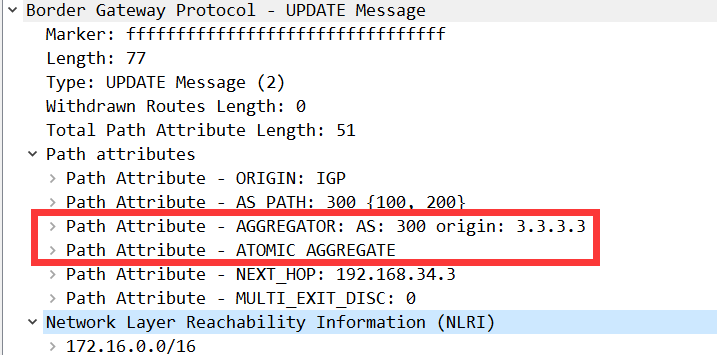
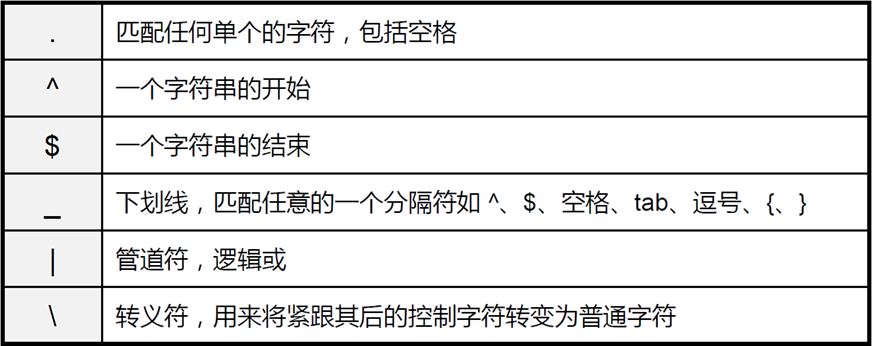
BGP正则匹配
- 之前我们只需要匹配IP地址,可以用到通配符或者前缀长度来匹配,现在BGP的属性大都是各种字符,并不是固定长度的数字
- 在BGP中如果想自定义匹配任何属性,可以直接将属性当作字符串来进行匹配
- 匹配字符串在计算机中可以使用正则表达式
下面我们用AS_PATH匹配来讲解BGP中的正则表达式

上面汇总的实验拓扑,我们在R4上配置,让起源于AS200的条目不学习
R4(config)#ip as-path access-list 1 deny _200$
R4(config)#ip as-path access-list 1 permit .*
R4(config)#router bgp 400
R4(config-router)#nei 192.168.34.3 filter-list 1 inBGP能使用的过滤路由手段
BGP汇总路由拆分
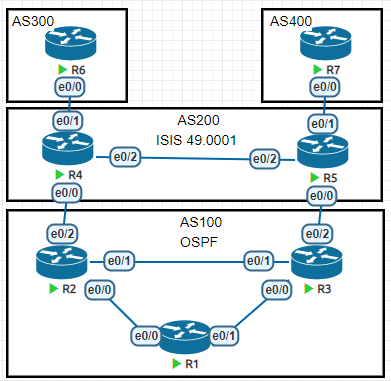
按照拓扑配置好全网,要求用环回接口建立邻居,R1是AS100的反射器,每个路由器都将lo0宣告进BGP
R6上配置
172.16.1.0/24环回接口,R7上配置172.16.2.1/24环回接口,并且宣告进BGP在AS200中对172.16开头的地址进行汇总,要求AS100能学到汇总路由
在R2和R3上对汇总路由进行拆分,让R1又能学习到明细路由
需求1
=========R1===========
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 route-reflector-client
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 3.3.3.3 route-reflector-client
=========R2===========
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
ip address 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 2.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 next-hop-self
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 200
neighbor 4.4.4.4 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 4.4.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.24.4
=========R3===========
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.13.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.23.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
ip address 192.168.35.3 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 3.3.3.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 next-hop-self
neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote-as 200
neighbor 5.5.5.5 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 5.5.5.5 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 5.5.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.35.5
=========R4===========
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.24.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.46.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
ip address 192.168.45.4 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
router isis
net 49.0001.0000.0000.0004.00
is-type level-2-only
!
router bgp 200
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 4.4.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 2.2.2.2 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote-as 200
neighbor 5.5.5.5 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 5.5.5.5 next-hop-self
neighbor 6.6.6.6 remote-as 300
neighbor 6.6.6.6 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 6.6.6.6 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 2.2.2.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.24.2
ip route 6.6.6.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.46.6
=========R5===========
interface Loopback0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.35.5 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.57.5 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/2
ip address 192.168.45.5 255.255.255.0
ip router isis
!
router isis
net 49.0001.0000.0000.0005.00
is-type level-2-only
!
router bgp 200
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 5.5.5.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 3.3.3.3 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 200
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 next-hop-self
neighbor 7.7.7.7 remote-as 400
neighbor 7.7.7.7 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 7.7.7.7 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 3.3.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.35.3
ip route 7.7.7.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.57.7
=========R6===========
interface Loopback0
ip address 6.6.6.6 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.46.6 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 300
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 6.6.6.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 200
neighbor 4.4.4.4 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 4.4.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.46.4
=========R7===========
interface Loopback0
ip address 7.7.7.7 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.57.7 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 7.7.7.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 5.5.5.5 remote-as 200
neighbor 5.5.5.5 ebgp-multihop 255
neighbor 5.5.5.5 update-source Loopback0
!
ip route 5.5.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.57.5需求2
R6(config)#int lo10
R6(config-if)#ip add 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0
R6(config-if)#router bgp 300
R6(config-router)#net 172.16.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0R7(config)#int lo10
R7(config-if)#ip add 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0
R7(config-if)#router bgp 400
R7(config-router)#net 172.16.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0需求3
R4
router bgp 200
aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 as-set summary-onlyR5
router bgp 200
aggregate-address 172.16.0.0 255.255.0.0 as-set summary-only但是这样做完了以后,我们发现R4无法学习R7的条目,R5也无法学习R6的条目
R4
access-list 1 permit 172.16.1.0
route-map R5out permit 10
match ip address 1
router bgp 200
neighbor 5.5.5.5 unsuppress-map R5outR5
access-list 1 permit 172.16.2.0
route-map R4out permit 10
match ip address 1
router bgp 200
neighbor 4.4.4.4 unsuppress-map R4out然后R4和R5需要针对R6和R7取消对应条目的抑制
R4
access-list 2 permit 172.16.2.0
route-map R6out permit 10
match ip address 2
router bgp 200
neighbor 6.6.6.6 unsuppress-map R6outR5
access-list 2 permit 172.16.1.0
route-map R7out permit 10
match ip address 2
router bgp 200
neighbor 7.7.7.7 unsuppress-map R7out需求4
R2
ip prefix-list huizong seq 5 permit 172.16.0.0/16
ip prefix-list mingxi seq 5 permit 172.16.1.0/24
ip prefix-list xiayitiao seq 5 permit 4.4.4.4/32
route-map RP_huizong permit 10
match ip address prefix-list huizong
match ip route-source xiayitiao
route-map RP_mingxi permit 10
set ip address prefix-list mingxi
set community 100:200 no-export
router bgp 100
bgp inject-map RP_mingxi exist-map RP_huizong copy-attributesR3
ip prefix-list huizong seq 5 permit 172.16.0.0/16
ip prefix-list mingxi seq 5 permit 172.16.2.0/24
ip prefix-list xiayitiao seq 5 permit 5.5.5.5/32
route-map RP_huizong permit 10
match ip address prefix-list huizong
match ip route-source xiayitiao
route-map RP_mingxi permit 10
set ip address prefix-list mingxi
set community 100:200 no-export
router bgp 100
bgp inject-map RP_mingxi exist-map RP_huizong copy-attributesBGP选路原则(面试官最爱)
- 最大weight
- 最大Local_Pref
- 优选起源于本地的路由
- 优选AS_PATH最短的路由
- ORIGIN
- 优选MED最小的路由
- 优选EBGP邻居的路由
- 优选到NEXT_HOP最近的路由
- BGP负载均衡(默认BGP不开启负载均衡)
- 优选最老的EBGP邻居的路由(根据邻居建立的时间判断)
- 优选RouterID最小的BGP邻居的路由
- 优选Cluster_List最短的路由
- 选择邻居IP地址最小的路由
BGP非等价负载均衡
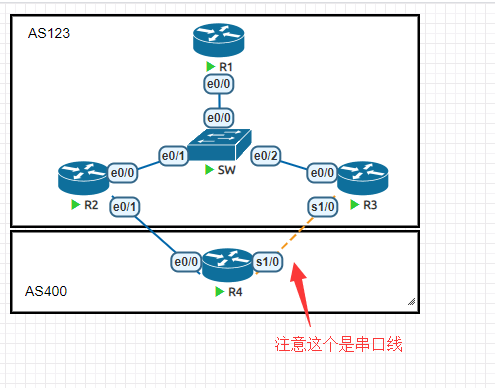
初始配置,R1作为路由反射器,R1和R4的lo0接口宣告进BGP
========R1=========
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.123.1 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
router bgp 123
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 remote-as 123
neighbor 2.2.2.2 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 2.2.2.2 route-reflector-client
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 123
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 3.3.3.3 route-reflector-client
========R2=========
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.123.2 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.24.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 123
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 123
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 next-hop-self
neighbor 192.168.24.4 remote-as 400
========R3=========
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.123.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 192.168.34.3 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 123
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 1.1.1.1 remote-as 123
neighbor 1.1.1.1 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 1.1.1.1 next-hop-self
neighbor 192.168.34.4 remote-as 400
========R4=========
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.24.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface Serial1/0
ip address 192.168.34.4 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 400
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 4.4.4.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 192.168.24.2 remote-as 123
neighbor 192.168.34.3 remote-as 123检查R1和R4是否学习到彼此
R1#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i 4.4.4.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 400 i
*>i 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 400 i
R4#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 1.1.1.0/24 192.168.34.3 0 123 i
*> 192.168.24.2 0 123 i
*> 4.4.4.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i让R4将去往1.1.1.0的两条路线全部用起来
ebgp非等价负载均衡,让R4根据两个邻居接口的带宽来分配流量
R4
router bgp 400
bgp dmzlink-bw
neighbor 192.168.24.2 dmzlink-bw
neighbor 192.168.34.3 dmzlink-bw
maximum-paths 2检查路由表,发现去往1.1.1.0/24已经实现非等价负载均衡,非等价比例为37:240
R4#show ip route bgp
1.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 1.1.1.0 [20/0] via 192.168.34.3, 00:01:56
[20/0] via 192.168.24.2, 00:01:56
R4#show ip route 1.1.1.0
Routing entry for 1.1.1.0/24
Known via "bgp 400", distance 20, metric 0
Tag 123, type external
Last update from 192.168.24.2 00:02:13 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 192.168.34.3, from 192.168.34.3, 00:02:13 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 37
AS Hops 1
Route tag 123
MPLS label: none
192.168.24.2, from 192.168.24.2, 00:02:13 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 240
AS Hops 1
Route tag 123
MPLS label: noneibgp非等价负载均衡
要让R1可以知道R2R3对AS400的链路带宽,才能做出非等价负载均衡的判断
R2
router bgp 123
bgp dmzlink-bw
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community extended
neighbor 192.168.24.4 dmzlink-bwR3
router bgp 123
bgp dmzlink-bw
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community extended
neighbor 192.168.34.4 dmzlink-bwR1
router bgp 123
bgp dmzlink-bw
maximum-paths ibgp 2检查R1的路由表负载均衡情况
R1#show ip route bgp
4.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 4.4.4.0 [200/0] via 3.3.3.3, 00:00:10
[200/0] via 2.2.2.2, 00:00:10
R1#show ip route 4.4.4.0
Routing entry for 4.4.4.0/24
Known via "bgp 123", distance 200, metric 0
Tag 400, type internal
Last update from 2.2.2.2 00:00:27 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 3.3.3.3, from 3.3.3.3, 00:00:27 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 37
AS Hops 1
Route tag 400
MPLS label: none
2.2.2.2, from 2.2.2.2, 00:00:27 ago
Route metric is 0, traffic share count is 240
AS Hops 1
Route tag 400
MPLS label: noneCost Community
- Cost Community是一个扩展的Community属性,只能传递给iBGP邻居或联邦peer(含联邦iBGP及联邦eBGP邻居),不能传递给eBGP邻居;
- 通过利用Cost Community,我们能够在一个AS或联邦内部自定义BGP的最优路径选择。Cost Community事实上是提供给我们除了“BGP13条选路规则”之外的又一“插入点”( point of insertion),相当于提供给我们另一个操控路由优选的手柄。
pre-bestpath(可以无视一切选路选择,强行修改路线)
- 最大weight
- 最大Local_Pref
- 优选起源于本地的路由
- 优选AS_PATH最短的路由
- ORIGIN
- 优选MED最小的路由
- 优选EBGP邻居的路由
- 优选到NEXT_HOP最近的路由
IGP(可以在负载均衡之前加上优选规则)
- BGP负载均衡(默认BGP不开启负载均衡)
- 优选最老的EBGP邻居的路由(根据邻居建立的时间判断)
- 优选RouterID最小的BGP邻居的路由
- 优选Cluster_List最短的路由
- 选择邻居IP地址最小的路由
- cost community是由CostID和CostValue组成
- 比较的时候,会从CostID=1开始比较CostValue越小越优
- 比如某条路由从R1学来携带1:9,从R2学来携带1:10,那么选择R1
- 比如某条路由从R1学来携带2:9,从R2学来携带1:10,那么还是从ID=1开始比较,而R1并没有携带ID=1,那么在比较的时候,R1的CostID=1的CostValue会使用默认值(2^32^/2)进行比较,最终选择R2
还原上面负载均衡用的实验环境
查看R1去往4.4.4.0/24的优选路线
R1#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i 4.4.4.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 400 i
* i 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 400 i修改下一跳为3.3.3.3的路由权重
R1(config)#router bgp 123
R1(config-router)#nei 3.3.3.3 weight 10
R1(config-router)#do clea ip bgp * so in
R1(config-router)#do sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i 4.4.4.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 400 i
*>i 3.3.3.3 0 100 10 400 i在R2上配置cost communtiy,将R1的路由选择改回来,从2.2.2.2走
R2
access-list 1 permit 4.4.4.0
route-map cost permit 10
match ip address 1
route-map cost permit 20
router bgp 123
neighbor 1.1.1.1 send-community extended
neighbor 1.1.1.1 route-map cost out到R1上查看这条路由
R1#sh ip bgp 4.4.4.0
BGP routing table entry for 4.4.4.0/24, version 5
Paths: (2 available, best #1, table default)
Advertised to update-groups:
1
Refresh Epoch 3
400, (Received from a RR-client)
2.2.2.2 (metric 11) from 2.2.2.2 (2.2.2.2)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, valid, internal, best
Extended Community: Cost:pre-bestpath:1:10
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0x0
Refresh Epoch 2
400, (Received from a RR-client)
3.3.3.3 (metric 11) from 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3)
Origin IGP, metric 0, localpref 100, weight 10, valid, internal
rx pathid: 0, tx pathid: 0
R1#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i 4.4.4.0/24 2.2.2.2 0 100 0 400 i
* i 3.3.3.3 0 100 10 400 i能不能在R1上配置一些命令,让R1拒收这个扩展团体属性?
BGP联邦
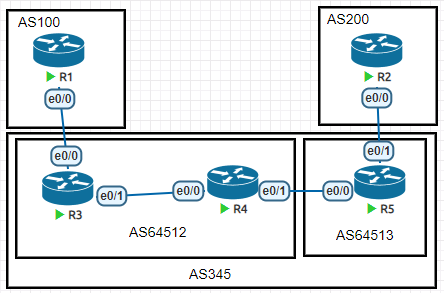
基础配置
=======R1========
interface Loopback0
ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.13.1 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 100
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 1.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 192.168.13.3 remote-as 345
=======R2========
interface Loopback0
ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.25.2 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 200
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 2.2.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 192.168.25.5 remote-as 345
=======R3========
interface Loopback0
ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.13.3 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.34.3 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
router bgp 64512
bgp log-neighbor-changes
bgp confederation identifier 345
neighbor 4.4.4.4 remote-as 64512
neighbor 4.4.4.4 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 4.4.4.4 next-hop-self
neighbor 192.168.13.1 remote-as 100
=======R4========
interface Loopback0
ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.34.4 255.255.255.0
ip ospf 1 area 0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.45.4 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 64512
bgp log-neighbor-changes
bgp confederation identifier 345
bgp confederation peers 64513
neighbor 3.3.3.3 remote-as 64512
neighbor 3.3.3.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 3.3.3.3 next-hop-self
neighbor 192.168.45.5 remote-as 64513
neighbor 192.168.45.5 next-hop-self
=======R5========
interface Loopback0
ip address 5.5.5.5 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/0
ip address 192.168.45.5 255.255.255.0
!
interface Ethernet0/1
ip address 192.168.25.5 255.255.255.0
!
router bgp 64513
bgp log-neighbor-changes
bgp confederation identifier 345
bgp confederation peers 64512
neighbor 192.168.25.2 remote-as 200
neighbor 192.168.45.4 remote-as 64512
neighbor 192.168.45.4 next-hop-self注意路由在BGP联邦内部传递的时候,很多属性不会发生变化,比如下一跳属性,比如本地优先级属性
并且在联邦内部的AS_PATH会用()表示内部的AS号,在离开联邦的时候,会将()替换为联邦的AS号
R5#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 1.1.1.0/24 3.3.3.3 0 100 0 (64512) 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 192.168.25.2 0 0 200 iR2#sh ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 1.1.1.0/24 192.168.25.5 0 345 100 i
*> 2.2.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i综合小实验
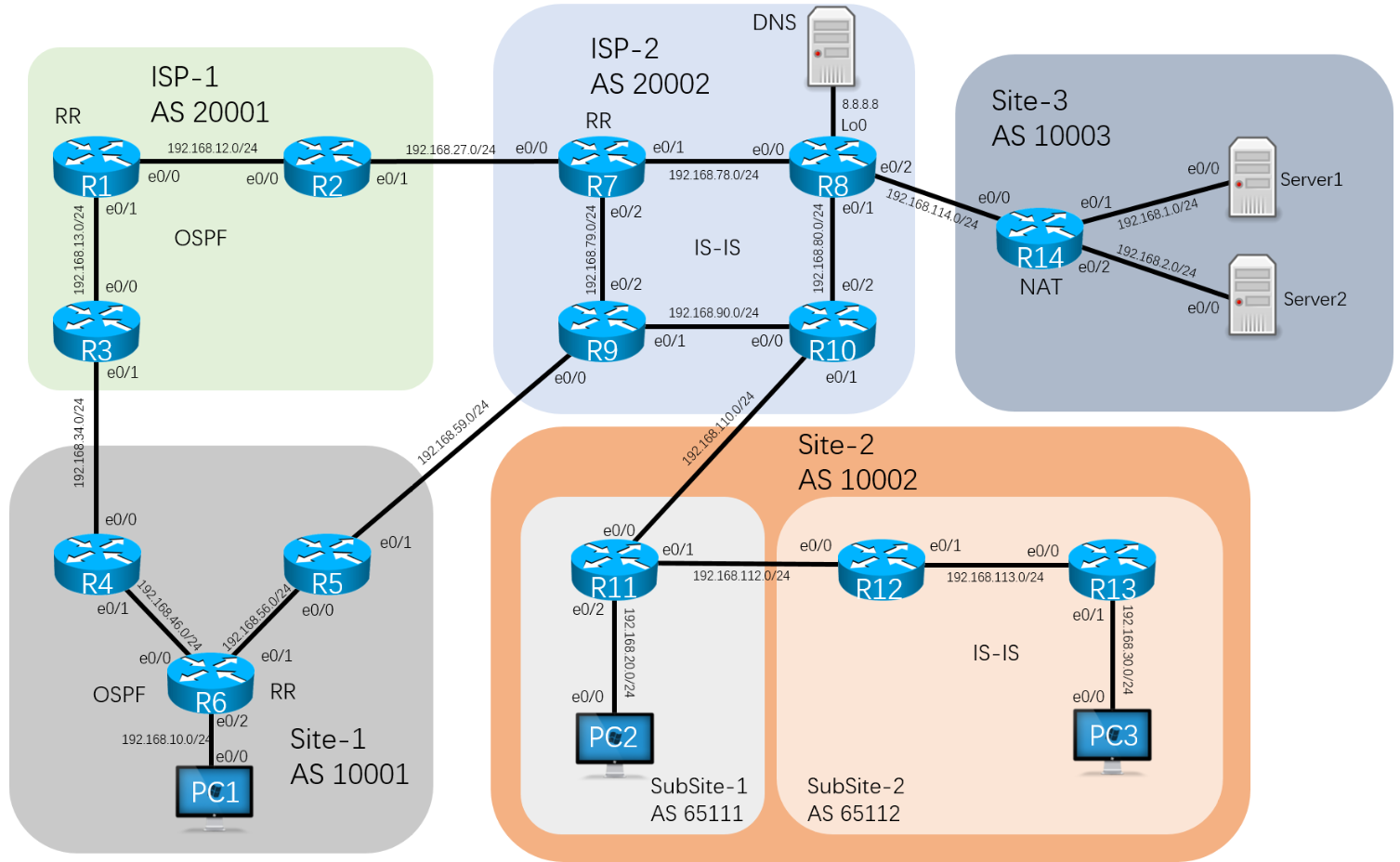
1、按照如图所示配置好接口的IP地址,在每台路由器上配置loopback0接口,地址为x.x.x.x(x为路由器编号)。所有的PC和Server的IP地址,都要通过8.8.8.8来DHCP获得。
2、路由器R1、R2、R3配置ospf保障loopback0可达性。路由器R4、R5、R6配置ospf保障loopback0可达性。
3、路由器R7、R8、R9、R10配置IS-IS区域为49.0001,保障loopback0可达性。路由器R12、R13配置IS-IS区域为49.0001,保障loopback0可达性。
4、按照如图所示配置好BGP区域20001、20002、10001、10002、10003,要求全部使用loopback0作为bgp的router-id,和用来建立邻居关系。
5、其中AS10002内部含有两个联邦成员,分别为65111和65112。
6、在R14上宣告192.168.114.0/24进BGP。R6、R11、R13分别向BGP宣告PC所在的网段。R8宣告loopback0进BGP。
7、在R14上做NAT,保障Server1和Server2可以访问8.8.8.8,并且当telnet 192.168.114.14的1111端口的时候,是Server1来回应,2222端口是Server2来回应。
8、在R8上添加A类解析domain.com域名到192.168.114.14。在每台PC上测试telnet domain.com 1111和2222。确保可以正常访问Server1和Server2。
9、在R13上添加loopback10接口,地址为130.130.130.130/24,并且宣告进BGP。要求该路由不能被除了AS10002以外的区域学习到。
10、在R14上创建lo10、lo20、lo30、地址为172.16.10.1/24、172.16.20.1/24、172.16.30.1/24。要求在AS10002中只能看到汇总路由,并且该汇总路由保留as_path属性。其他AS可以看到明细路由。
11、通过as-path access-list在R11上过滤起源于AS10001的路由。并且在R6和R1上重分布外部路由进行测试。
12、在AS10001中,默认所有的路由都从R4离开AS,只有8.8.8.0/24这条路由是从R5离开AS的,在PC1上进行测试。
13、要求R13能学习到172.16.0.0这条汇总路由的明细,并且当172.16.0.0/16出现故障的时候,R13上的明细也能消失。

